DDPM
1. Introduction
- The research area covered by the paper
- Image Generation
- Limitations of previous studies in this task
-
GAN (Generative Adversarial Networks)
- Structural flaws in adversarial architectures:
- The learning process is incomplete and can be easliy disrupted by experimental factors.
- GANs are unable to generate a diverse range of images.
- Structural flaws in adversarial architectures:
-
VAE (Variational Autoencoder)
- Limited feature representation:
- Images generated by VAEs lack detail and often appear blurry.
- VAEs struggle to model complex data distribution.
- There is a trade-off: higher image quality often leads to lower diversity.
- Limited feature representation:
-
Autoregressive model (ex. PixelCNN, PixelRNN)
- Extreamely high computational cost.
- Contributions
- Learning stability
- Quality of the samples
- Diversity
2. Related Work
Skip
3. Methodology
Main Idea
The authors propose an architecture of Diffusion Models.
- Forward Process
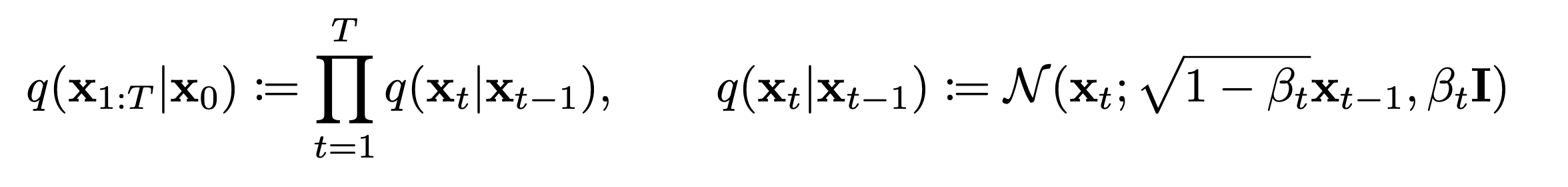
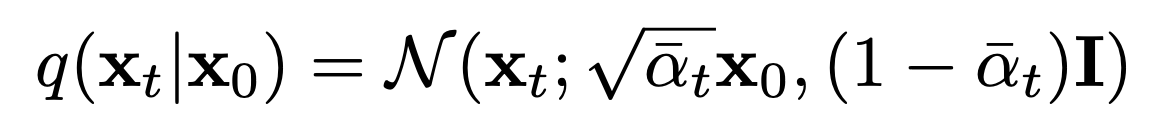
Why?

Q) Why did they use these alpha and beta? A) There are sevaral methods to make Markov Chain converge to a normal distribution. The authors simply chose this approach, likely because it showed the best performance.
Q) Why do they use a standard normal distribution? A) For convenience. A standard normal distribution is the easiest to work with.
-
Reverse Process
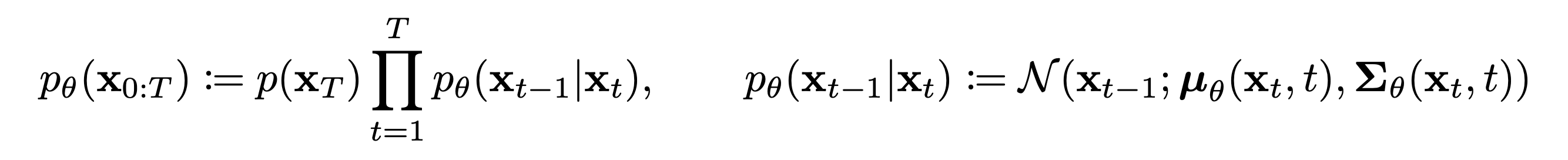
-
Loss The ELBO

Derivation of Loss
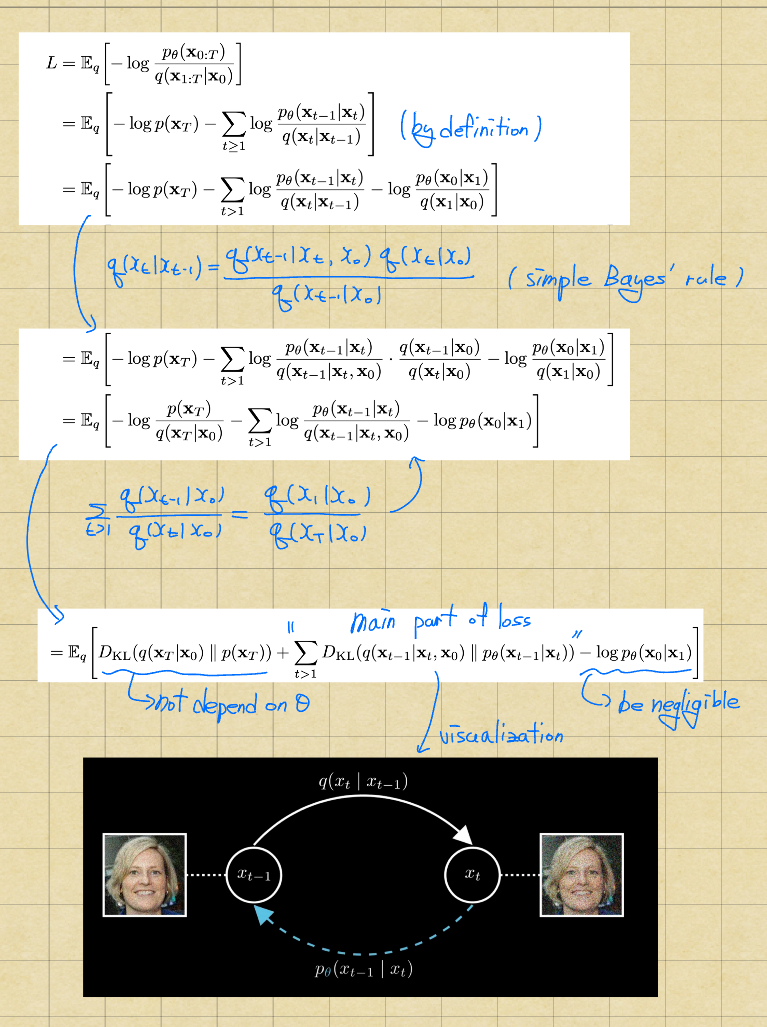
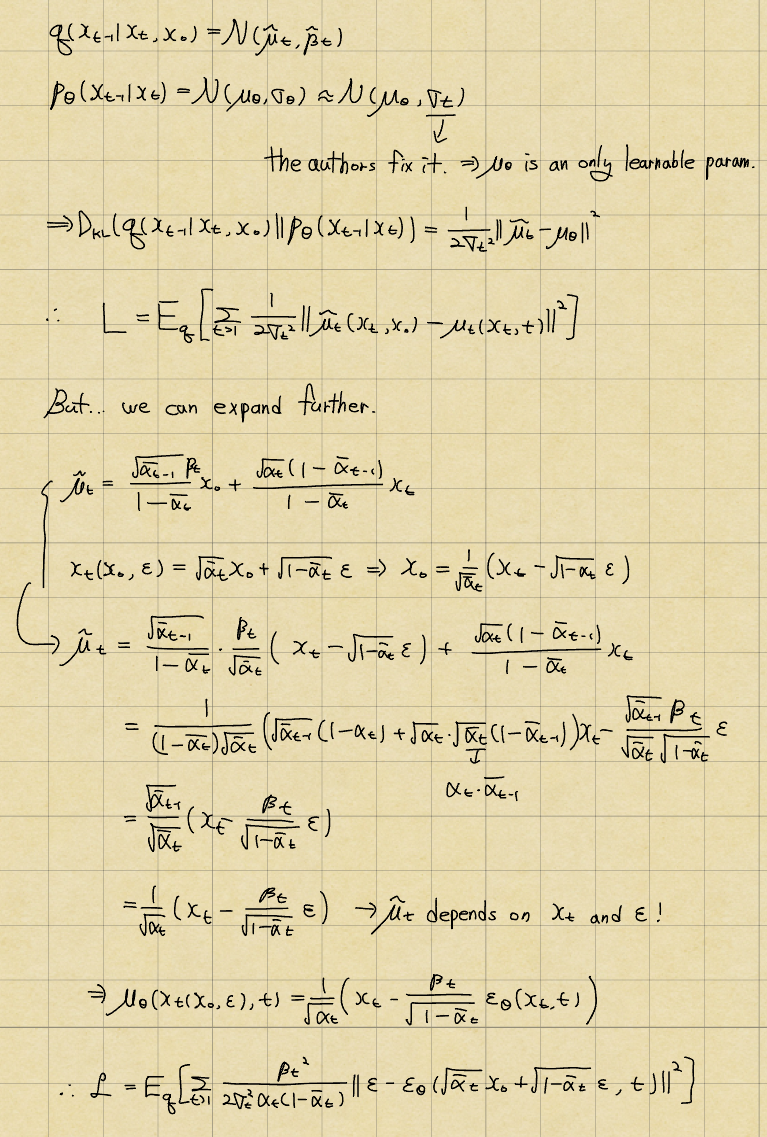
As a result, the loss only depends on the noise(epsilon)! This makes it quite simple and convenient.
(The paper states that) To summarize, we can train the reverse process mean function approximator mu_theta to predict mu tilda_t, or by modifying its parameterization, we can train it to predict epsilon.
-
Data scaling, Reverse process decoder, and L0
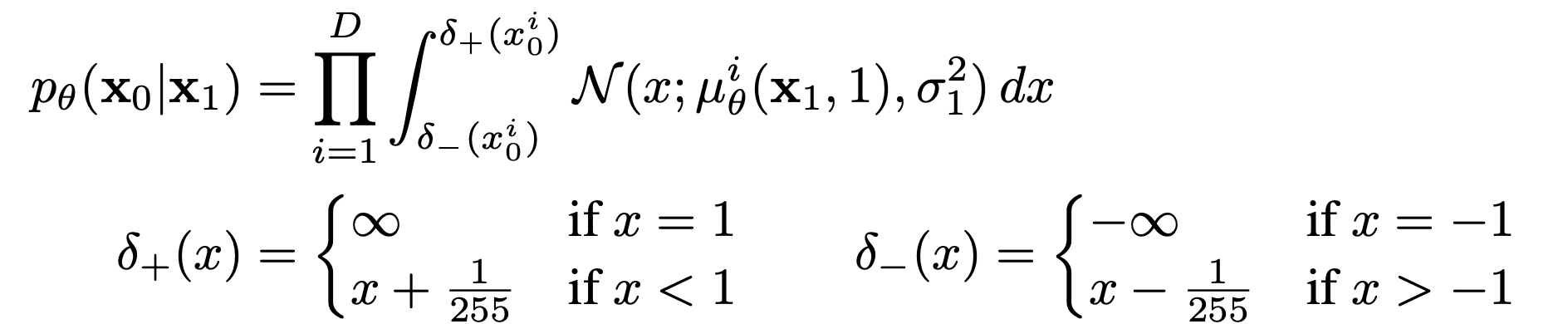
-
Real-Training Objective (the Loss)
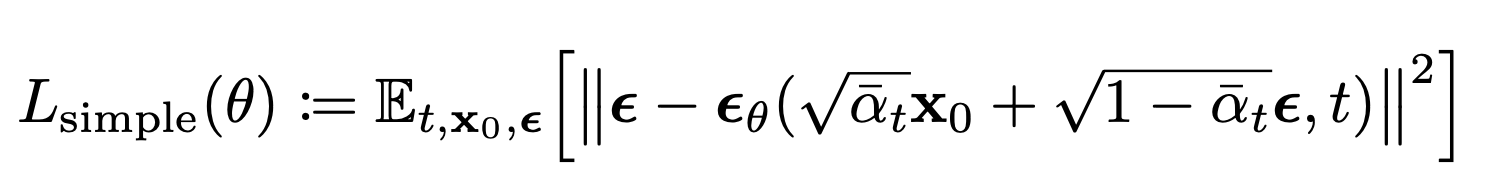 The authors remove parameters that depend on t, which improves performance.
(The paper states that) These terms train the network to denoise data with very small amounts of noise, so it is beneficial to down-weight them so that the network can focus on more difficult denoising tasks at larger terms. We will see in our experiments that this reweighting leads to better sample quality.
The authors remove parameters that depend on t, which improves performance.
(The paper states that) These terms train the network to denoise data with very small amounts of noise, so it is beneficial to down-weight them so that the network can focus on more difficult denoising tasks at larger terms. We will see in our experiments that this reweighting leads to better sample quality.
With this objective, DMs are trained using the following algorithm:
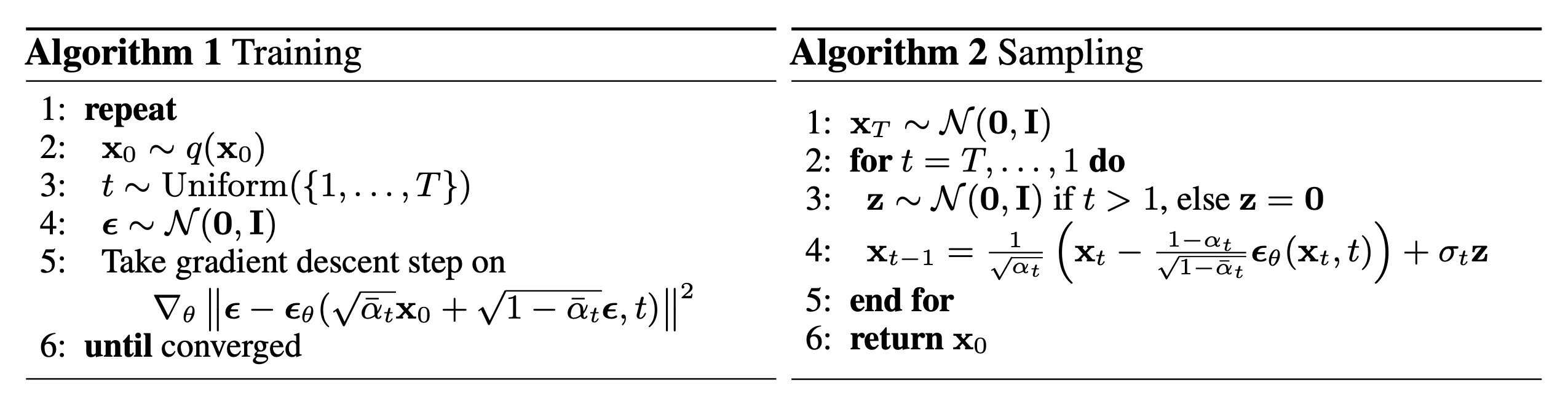 During training, it is sufficient to select only a few values of (t) from 1 to (T). Then, the gradient of L_simple can be calculated based on (x_0), and the model is updated using this gradient for backpropagation.
During training, it is sufficient to select only a few values of (t) from 1 to (T). Then, the gradient of L_simple can be calculated based on (x_0), and the model is updated using this gradient for backpropagation.
4. Experiments and Results
Datasets
CIFAR10 (Candian Institute For Advanced Research)
Results
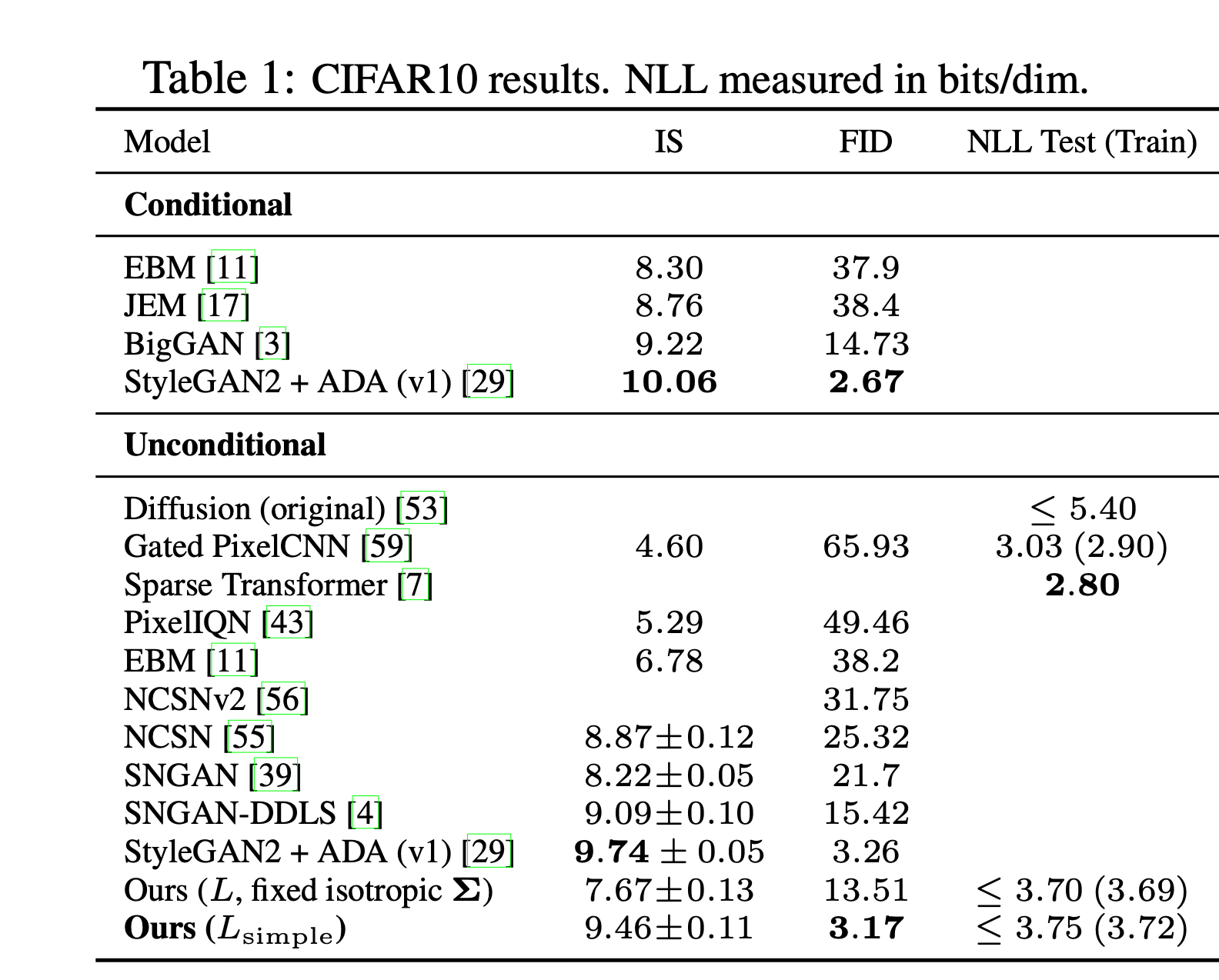
The simple objective used in DMs works well!
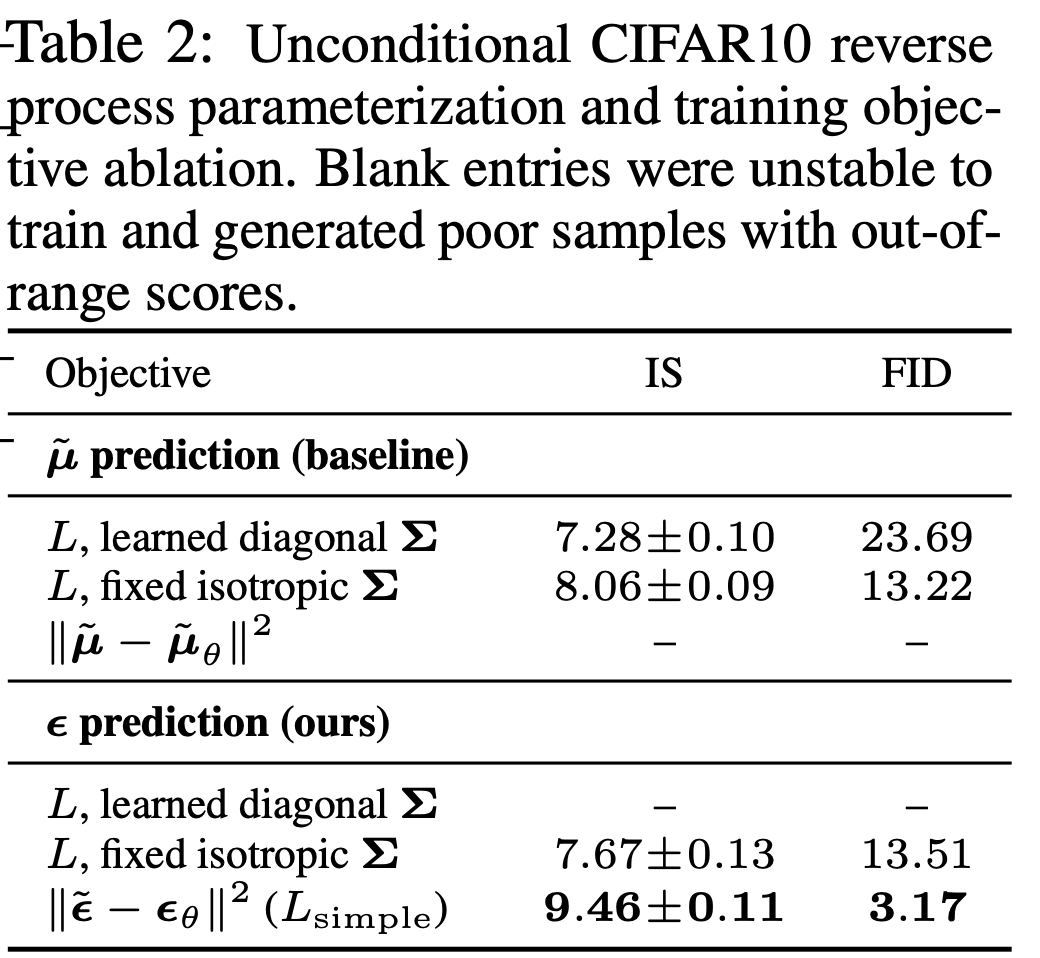 Furthermore, reparameterizing from from mu to eplsion leads to even better performance.
Furthermore, reparameterizing from from mu to eplsion leads to even better performance.
After this, the authors discuss progressive coding and generation based on information theory. Since I don't have much background in these topics, I asked AI for clarification.
(In Korean)
Progressive Coding 파트 핵심 요약
- **Diffusion 모델의 샘플 생성 과정을 정보이론적으로 해석**
→ 이미지를 여러 단계(timestep)에 걸쳐 점진적으로 압축하고 복원하는 과정으로 본다.
- **각 단계별로 필요한 정보량(KL divergence)을 계산**
→ 전체 압축 효율(rate)과 손실(distortion)을 평가할 수 있다.
- **알고리즘적으로, 이미지를 점진적으로 노이즈화(encoding)하고,
다시 점진적으로 복원(decoding)하는 방식**
→ 이 과정에서 필요한 정보만 코드로 저장/전송하면 효율적인 손실 압축이 가능하다.
- **결론:**
Diffusion 모델은 "점진적 손실 압축기(progressive lossy compressor)"로 해석할 수 있으며,
정보이론적 관점에서 rate-distortion trade-off를 분석할 수 있다.
---
Progressive Generation
- **핵심:**
Diffusion 모델의 샘플링(reverse process)은 이미지를 점진적으로 복원하는 과정이다.
- **의미:**
완전히 노이즈 상태에서 시작해, 여러 단계에 걸쳐 점점 더 선명한 이미지를 생성한다.
- **장점:**
중간 단계에서 이미지 품질을 조절하거나, 샘플링 속도를 개선할 수 있는 가능성이 있다.
---
Connection to Autoregressive Decoding
- **핵심:**
Diffusion 모델의 점진적 생성 방식은 Autoregressive 모델(예: PixelCNN, GPT 등)의 순차적 디코딩과 구조적으로 유사하다.
- **의미:**
두 모델 모두 데이터를 여러 단계/순서에 따라 생성한다.
- **인사이트:**
Diffusion 모델과 Autoregressive 모델의 장단점, 효율성, 품질을 비교/분석할 수 있는 연구적 연결고리를 제공한다.
Additional details can be found in the appendix.
Increasing the number of diffusion steps destroys more structure in the source images, which the model completes during the reverse process. This allows us to interpolate at both fine granularities and coarse granularities. In the limiting case of 0 diffusion steps, the interpolation mixes source images in pixel space. On the other hand, after 1000 diffusion steps, source information is lost and interpolations are novel samples.

5. Conclusions
-
What a creative and marvelous process of induction. How do the authors come up with ideas like this?
-
There is a fundamental difference between the NLP and image domains.
- In most cases, NLP uses cross-entropy loss
- In image generation, models use KL divergence, which effectively removes the original data distribution from corss-entropy.
- Natural language is highly structured, so we can assume that the real data distribution can be approximated from samples.
- However, in image gerenation, we have no information about the distribution of the original images.
- Therefore, KL divergence in used to eliminate the unknown original distribution.
-
A fundamental difference between NLP and Image field.
- Most cases, NLP uses cross-entropy.
- In image generation field, models adopt KL divergence, which remove the original data distribution from cross-entropy
- Natural language is quite structural. So, there is a premise that we can approximate the real data distribution from the samples.
- But in image generation, we don't have any information about origin images.
- Therefore, we have to use KL divergence with removing the origin distribution.
- It tells us some zero-shot CLIP's capability.
- Only one image is inadequate to learn the image distribution, not like NLP.
- e.t.c., a 'cat' word and a 'cat image'. Person who have been seeing cat, can't distinguish the cat from the image, containing the background and other obejcts.